
In this blog, we’ll take you on a journey through Apple Vision Pro, an exciting technology that brings digital experiences to life. We’ll share our experience and discoveries while working on a Proof of Concept (PoC) project and explore the process of moving existing apps to this new platform. We’ll also discuss which types of apps are best suited for this technology. During our exploration, we’ll tell you about what we’ve noticed, the challenges we’ve faced, and the exciting things we’ve learned, giving you a clear picture of how this amazing technology works.
The Technology Behind Apple Vision Pro
Unveiled at the latest WWDC event, Apple Vision Pro introduces us to a world of immersive experiences that reshape how users interact with digital environments through Spaces. Apps can employ windows and volumes to showcase content, but for a more captivating experience, they can open a dedicated Full Space, where only its content will be visible. Within this space, apps can wield windows and volumes, craft limitless 3D content, establish portals to different worlds, or fully immerse users in captivating environments.
Empowering developers, Apple Vision builds upon the advanced SDK known as Reality Kit, now enriched with even more features that enhance the creation of immersive experiences. This includes the ability to craft realistic lighting, create convincing shadows, design captivating portals, and deploy stunning visual effects, taking the visual quality of AR and MR experiences to new heights. These enhancements make crafting immersive experiences more accessible and visually striking than ever before.
Apple further streamlines content creation with Reality Composer Pro, simplifying the design of scenes featuring 3D models. Apple's contribution extends to transforming 3D models into the highly compatible USDZ format facilitated by the versatile Reality Converter.
Our Devs Experience With Apple Vision
In our exploration of Apple Vision, we set out to implement a Proof of Concept (PoC), a mini-project that loaded elements into an Immersive Space and allowed us to interact with them using gestures. We encountered challenges and valuable insights as we delved into this journey.
- Simulator Struggles: Our experience with the Vision Simulator has been somewhat turbulent. We've encountered instability even when attempting something as straightforward as running a basic "Hello World" app. Additionally, we've noticed that changing the scene of the simulator (for example, from Kitchen Day to Kitchen Night) didn't update the reflected lightning on the existing models in Space in real time; a simulator restart is needed.
- Hunting for Code Examples: Finding useful code snippets can be like searching through a confusing jungle of videos. The video descriptions can make this quest quite challenging because they describe the application they will implement instead of the functions used to achieve it.
- Simulator Limitations: The Vision Simulator has its limitations. It can't replicate ARKit features available on physical devices, such as plane detection and hand movement tracking. This serves as a reminder that the simulator has its boundaries, and real-world performance can differ.
- Texture Troubles in 3D Model Conversion: Reality Converter offers a streamlined process while transitioning 3D models, such as switching from .obj to .usdz. However, we encountered challenges, notably in dealing with texture-related issues during this conversion process.
Our Apple Vision journey showcases the dynamic nature of technology development. While we've faced challenges, these obstacles have only served as stepping stones for further exploration and understanding. We look forward to embracing more insights, overcoming hurdles, and unlocking Apple Vision's exciting possibilities.
It's important to acknowledge that getting a physical device for testing can be a logistical challenge in certain regions, thus emphasizing the reliance on the simulator. In the context of ARKit apps on iOS, we've traditionally favored real device testing due to the simulator's limitations in replicating real-world AR experiences. So, until Vision Pro becomes more accessible, this is a limitation of developing this type of app.
Migrating Existing Apps to visionOS
Apple Vision Pro offers a promising frontier for creating immersive applications, and the opportunity to transition existing apps to this innovative platform is exciting. While some apps may require substantial adjustments to meet Apple requirements, it’s important to note that in some cases, migrating to visionOS can be a seamless process, with little to no changes required.
Apple provides a checklist of prerequisites to evaluate whether your app is visionOS compatible. These requirements serve as a litmus test for readiness, ensuring a seamless migration process. Here are some key checkpoints to consider:
- App is Functional: Your app should smoothly launch and operate within the visionOS simulator without any glitches. The core functionality of your app must perform as expected, delivering a smooth user experience.
- No Bugs Are Exhibited: To ensure a smooth transition, it's vital that your app's features and functions work as intended without any issues. Any bugs or unexpected behaviors should be addressed and resolved to guarantee a smooth user experience.
- App Doesn't Make Capability Assumptions: It's important to verify that your app doesn't rely on specific device features or functions that may not be available on Apple Vision Pro. Compatibility should extend across the board to ensure that your app performs consistently across different platforms.
By adhering to these checklist requirements, you can set a strong foundation for migrating your existing app into the realm of visionOS.
Apple's commitment to delivering immersive experiences involves a rigorous evaluation of app compatibility with VisionPro. Developers can begin this evaluation by running and testing their apps in the visionOS simulator within Xcode.
Any issues that could impede Apple's evaluation can be identified and resolved using the compatibility checklist we provided. This collaborative effort ensures that the creation of robust, immersive applications aligns with Apple's vision for the future of technology. Participating in this evaluation process empowers developers to shape the landscape of immersive experiences on the VisionPro platform.
While the compatibility checklist is essential for migration to visionOS, certain guidelines can further optimize the user experience:
- Leverage Hover Interactions: Incorporate hover interactions using system components with built-in hover functionality or the hover effect API for SwiftUI and UIKit.
- Opt for Vector-Based Content: Prioritize vector graphics for scalable and sharp visuals across different devices.
- Camera and Microphone Considerations: Use DiscoverySession for hardware detection, especially for camera and microphone access in visionOS.
- Address UIKit Limitations: Be aware of UIKit limitations in visionOS, and adapt your app accordingly, excluding functionalities like UIDeviceOrientation, UIScreen, and UITabBar leading and trailing if necessary.
By following these guidelines, you can maximize the potential of visionOS, creating apps that provide users with a truly immersive and user-friendly experience. These considerations are instrumental in making the most of this cutting-edge platform and ensuring that your apps stand out in the world of extended reality.

Adapting ARKit-Based Apps for visionOS: Key Considerations.
When transitioning ARKit-based apps to visionOS, it's important to consider more than just the compatibility checklist. Here are key considerations to ensure a seamless integration of ARKit technology in visionOS:
- Adopt Common Technologies: To create an app that runs smoothly on iOS and visionOS, leverage the available technologies on both platforms. While ARKit in iOS offers a variety of interface creation options, visionOS prefers SwiftUI and RealityKit. If your app doesn't already use RealityKit for 3D content, it's advisable to make the switch before adding visionOS support. Retaining older technology code in your iOS app may necessitate recreating much of it using RealityKit when transitioning to visionOS.
- Convert to USDZ Format: In both iOS and visionOS, the recommended format for 3D assets is USDZ. This format streamlines your assets into a single file, encompassing models, textures, behaviors, physics, anchoring, and more. To ensure compatibility, utilize the Reality Converter tool provided with Xcode to convert your assets for your visionOS project.
- Update Your Interface: In visionOS, you control your app's content, and the system manages its integration with the user's surroundings. Unlike iOS, where a special ARKit view blends your content with live camera content, visionOS requires you to focus solely on your content, necessitating the removal of the special ARKit view.
- Replace ARKit Code: ARKit offers distinct APIs for iOS and visionOS, with different approaches for utilizing ARKit services. In iOS, you use ARKit to display your content and manage interactions with the surroundings. In visionOS, the system takes care of displaying your content, so ARKit primarily manages interactions with the surroundings. In fact, some visionOS apps may not require ARKit at all, except when specific services are needed, such as plane detection, image tracking, scene reconstruction, hand tracking, world tracking, and device-pose prediction.
- Isolate Unavailable ARKit Features: If your app relies on ARKit features that aren't supported in visionOS, isolate that code in the iOS version of your app. Features like face tracking, body tracking, and object detection are unavailable in visionOS, and must remain exclusive to the iOS version.
Adapting ARKit-based apps to visionOS can be complex, particularly for apps heavily relying on ARKit features. It's important to recognize that these apps, which already leverage augmented reality on iOS, may require the most work to bring to visionOS. The distinct APIs and approaches of ARKit in iOS and visionOS can present unique challenges during the transition.
Features like face tracking, body tracking, and object detection that are unavailable in visionOS must be carefully managed and retained in the iOS version. However, the opportunities in the immersive world of visionOS are promising for apps that can successfully make the switch.
Choosing the Right Apps for Migration: Where visionOS Shines
Migrating apps to visionOS isn't a one-size-fits-all approach; it's about identifying apps where the technology can truly elevate the user experience. The key to determining which apps are ideal candidates for migration lies in recognizing features that can benefit from extended reality (XR) interactions. Here are some essential considerations to guide your decision:
- Immersive Learning and Training: Educational and training apps can benefit significantly from migration to visionOS. Providing users with immersive experiences that allow them to learn, practice, or train in a virtual space can be a game-changer. Whether it's a medical training app, a language learning tool, or a virtual museum, visionOS can create a more engaging and interactive experience.
- Virtual Try-On and Shopping: E-commerce and retail apps can explore the potential of visionOS for virtual try-on experiences. Users can try on clothing, accessories, or even furniture in an immersive environment, helping them make more informed purchase decisions.
- Visualizing Architecture and Design: Apps related to architecture, interior design, or real estate can leverage visionOS to offer users a 3D view of spaces, enabling them to explore designs, layouts, and structures. This immersive visualization can aid in decision-making and planning.
- Collaborative and Social Apps: Apps that focus on collaboration and social interaction can use visionOS to create shared virtual spaces where users can meet, work, or play together. These experiences go beyond traditional video conferencing or chat applications.
- Gaming and Entertainment: Games and entertainment apps can benefit from the immersive nature of visionOS. Whether it's creating augmented reality (AR) games that blend seamlessly with the real world or providing users with interactive storytelling experiences, visionOS adds a new layer of engagement.
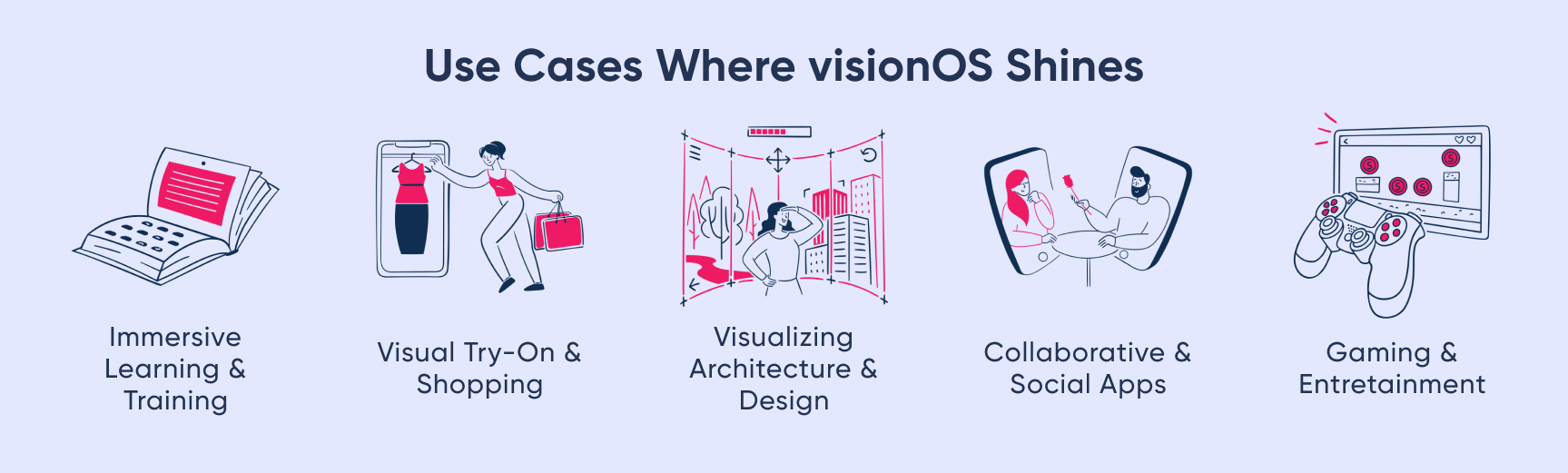
By identifying these features and use cases, you can pinpoint which apps benefit most from migration to visionOS. It's an opportunity to transform user experiences and harness the potential of extended reality in various industries and applications.
Conclusions
Apple Vision invites us to embark on a journey into the immersive world of extended reality. The introduction at WWDC was just the beginning, unveiling the innovative concept of Immersive Spaces and enhancing the development toolkit with Reality Kit and Reality Composer Pro. Our exploration, rooted in a Proof of Concept (PoC) project, has been a valuable learning experience.
Yet, it's essential to recognize the challenges. The Vision simulator, while promising, isn't without its instabilities, and missing features like ARKit plane tracking remind us of the technology's early stage. This pioneering venture into visionOS may not see immediate widespread adoption, but it promises an exciting future for those who dare to explore its potential.
Selecting the right apps for migration to visionOS is a nuanced decision driven by recognizing features that can truly shine in an extended reality context. While the technology may be in its infancy, the immersive experiences it offers keep us at the forefront of innovation. The vision of tomorrow is brimming with promise, and we're eager to continue our journey into this captivating realm of extended reality.
