
Much like electricity without power, AI lacks substance without quality data. Your data quality becomes the cornerstone determining the success of your AI solution. Envision Data Governance as the silent architect behind the AI revolution.
In this blog post, we highlight the critical role of data governance— the custodian ensuring every AI endeavor's reliability, ethics, and efficacy.
What is Data Governance
Data governance is the process of ensuring data is secure, private, accurate, available, and usable. It means setting internal standards—data policies—that apply to how data is gathered, stored, processed, and disposed of. It governs what kinds of data are under governance, who can take actions over what kinds of data, when, under which situations, and using which methods.
Goals of Data Governance
Break Down Organizational Data Silos
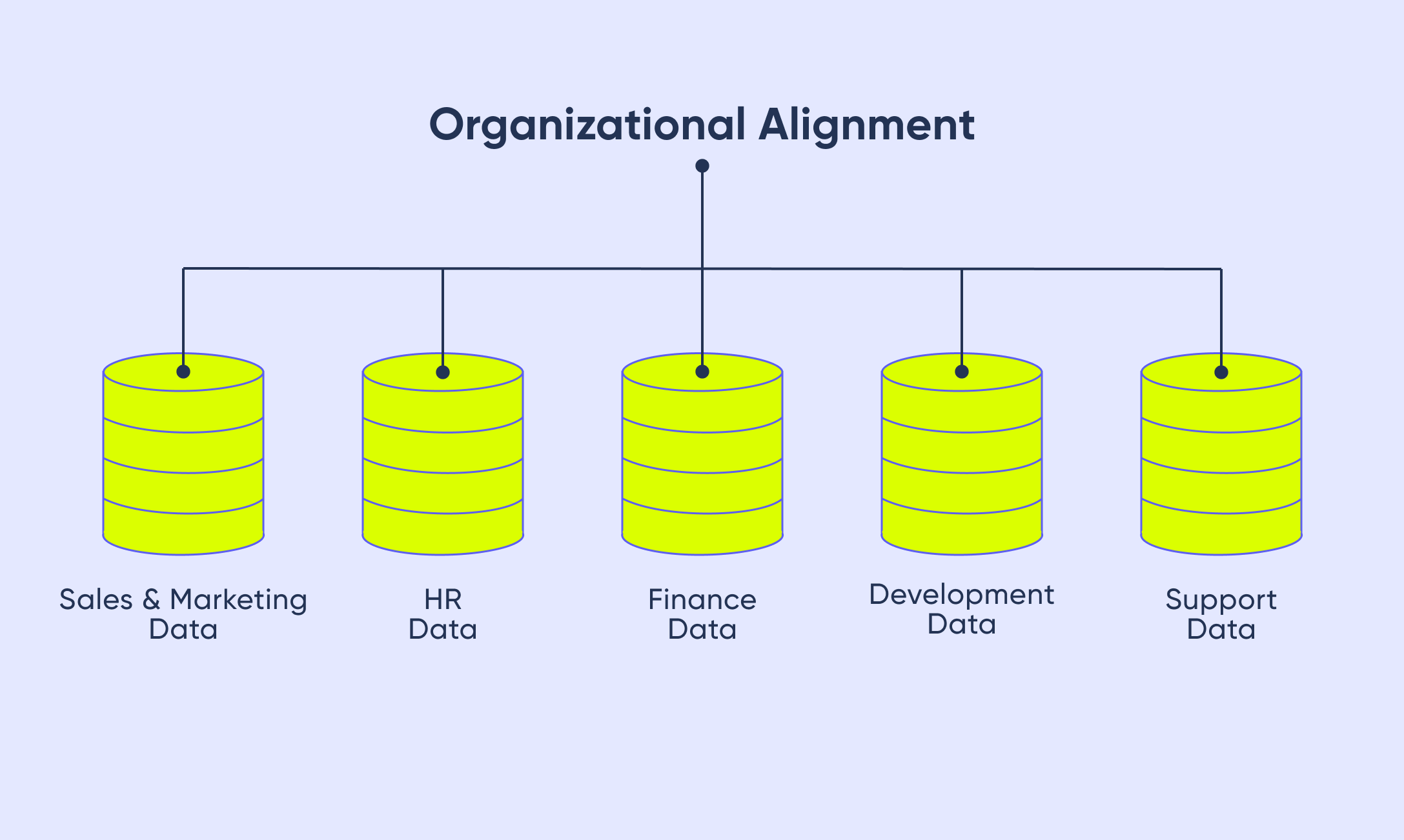
A key goal of data governance is to break down data silos in an organization. Such silos commonly build up when individual business units deploy separate transaction processing systems without centralized coordination or an enterprise data architecture. Data governance aims to harmonize the data in those systems through a collaborative process, with stakeholders from the various business units participating.
Have you thought why, when you call a service provider, they ask the same questions at every step of the process? That’s because those business units have their own data silos without proper coordination.
Ensuring Proper Data Utilization and Safeguarding Sensitive Information
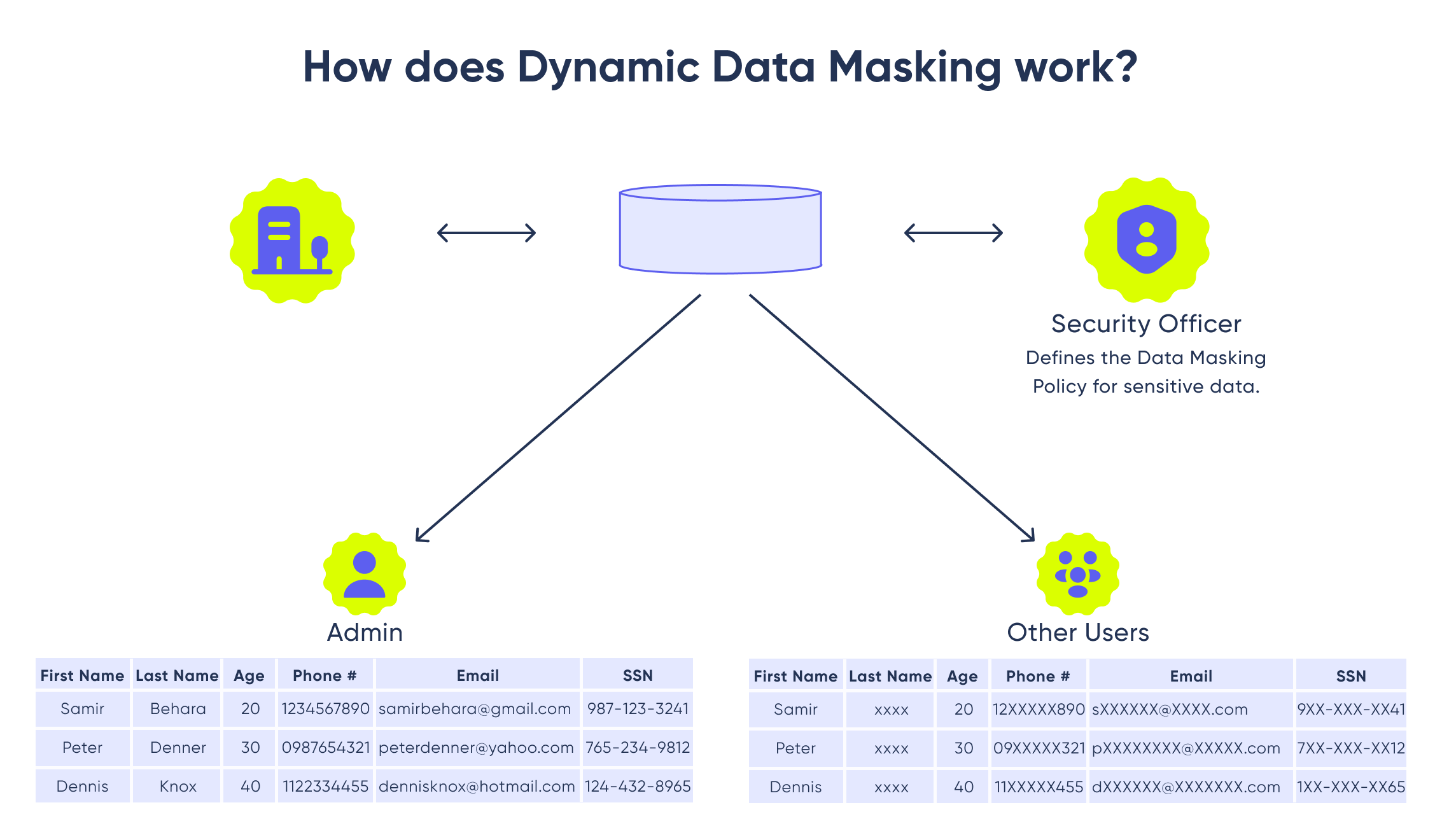
Another data governance goal is to ensure that data is used properly, both to avoid introducing data errors into systems and to block potential misuse of personal data about customers and other sensitive information. That can be accomplished by creating uniform policies on the use of data, along with procedures to monitor usage and enforce the policies continuously.
Consider the case of your organization dealing with sensitive information. You probably want the finance department to see only amounts without customer names or the customer service department to see names and SLAs without prices. All those types of rules could be defined and assured implementing Data Governance.
Data Governance in Action
Here are some common use cases:
- Data stewardship: Data governance often means giving accountability and responsibility for both the data itself and the processes that ensure its proper use to “data stewards”.
- Data quality: Data governance is also used to ensure data quality, which refers to any activities or techniques designed to make sure data is suitable to be used. Data quality is generally judged on six dimensions: accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, validity, and uniqueness.
- Data management: This is a broad concept encompassing all aspects of managing data as an enterprise asset, from collection and storage to usage and oversight, making sure it’s being leveraged securely, efficiently, and cost-effectively before it’s disposed of.
Risks of poor Data Governance
Poor data governance can lead to a wide range of risks and negative consequences for organizations. Some of the key risks of poor data governance include:
- Data Inaccuracies and Inconsistencies: Without proper governance, data may become inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent. This can lead to decision-making based on faulty information and erode trust in data.
- Compliance Violations: Failure to manage data compliant with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and legal requirements can result in legal fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
- Data Silos: Without governance, data may be stored and managed in isolated silos, making it difficult to share and access data across the organization. This can hinder collaboration and lead to inefficiencies.
- Data Redundancy: Lack of governance may result in duplicate or redundant data, leading to increased storage costs and confusion about which data is the "single source of truth.”
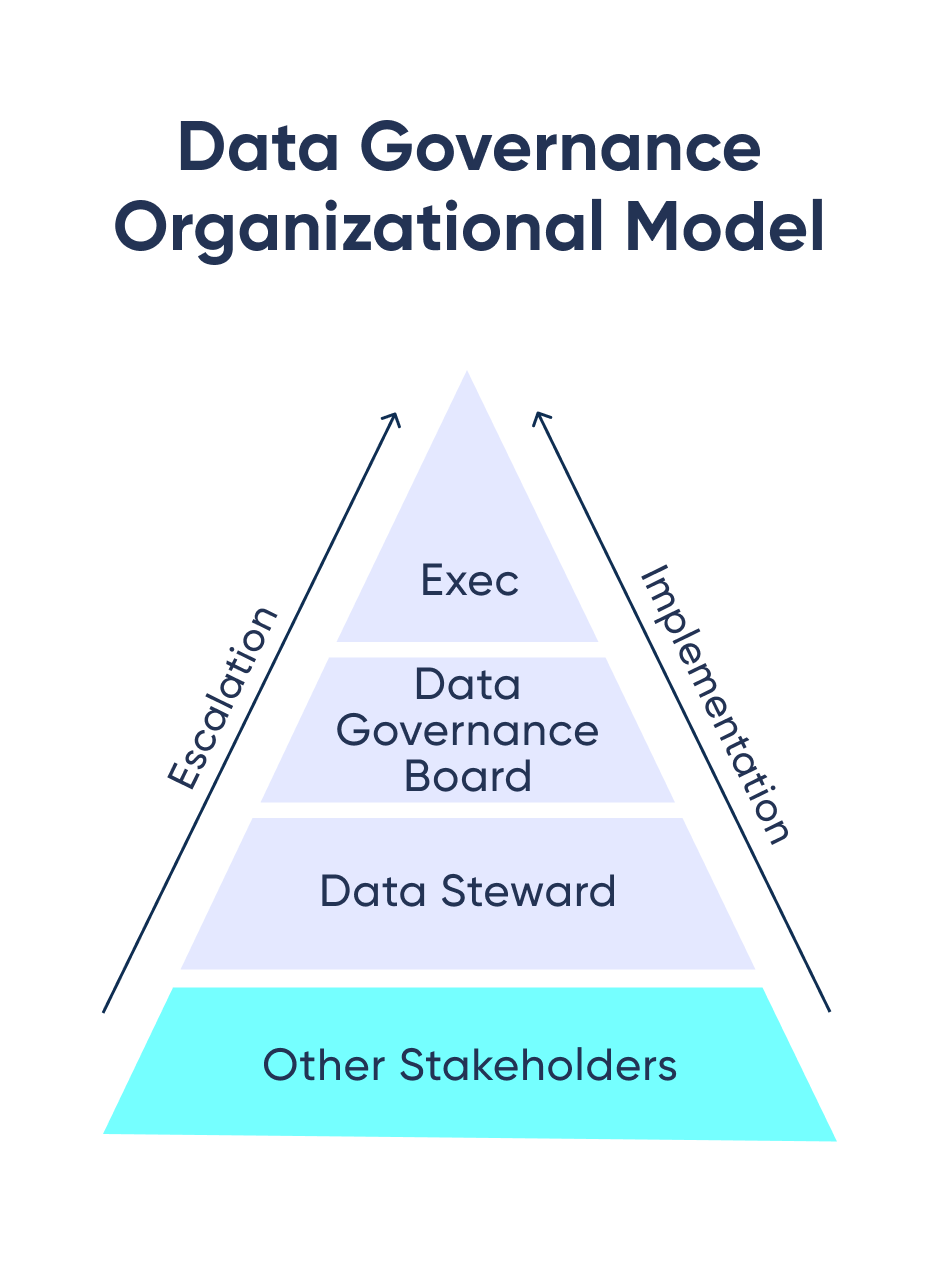
Roles and Responsibilities in Data Governance
Implementing a data governance process typically involves establishing a clear organizational structure to define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority for managing data. The specific structure can vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and culture, but here is a common framework for a data governance organizational structure:
- Data Governance Council: responsible for setting the strategic direction of data governance
- Data Governance Team: provides support for data governance activities, including policy creation, monitoring, and communication
- Data Stewards: They enforce data governance policies
- Data Owners: department heads who are responsible for specific datasets
- Data Users: people who access and use data as part of their job responsibilities
Challenges When Implementing Data Governance
Before initiating a Data Governance program, organizations must understand that some challenges will be faced during the process.
Lack of support
One of the initial challenges is getting buy-in and support from top management and employees. Many stakeholders may not fully grasp the importance of data governance, which can make it difficult to secure the necessary resources and commitment.
Resource Constraints
Establishing and maintaining a robust data governance framework requires a dedicated team, tools, and technology. Resource constraints, both in terms of budget and skilled personnel, can impede progress.
Cultural Resistance
Changing the culture and mindset within an organization is often necessary to instill a data-driven approach. Resistance to these cultural changes can be a substantial obstacle.
Sustainability
Data governance is not a one-time project but an ongoing process. Sustaining the effort and commitment over the long term can be difficult, especially in the face of shifting priorities and leadership changes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Data Governance
Data governance is an essential component of any organization's data management strategy. It serves as the framework that ensures data is accurate, secure, and compliant with regulations.
Throughout this blog post, we've explored the key elements of data governance, including why it is important to organizations, which are their goals, the responsibilities of each role, and more. We've also delved into the benefits of implementing data governance, which include increased trust in data, reduced data-related risks, and improved data utilization.
Stay tuned if you liked this brand new data team post. We will be writing about data governance tools available in the market and how they could be implemented in your organization.
If you're interested in a custom-made solution or would like to learn the most efficient way to handle your company's data, don't hesitate to reach out to our team!
Thanks for reading 🙂
💡 Learn the intricacies of AI and how to manage sensitive data responsibly to ensure safe AI innovation from leading experts!
Register now to secure your spot! ✅

