
We at Xmartlabs have built an expert team around computer vision, machine learning, and augmented reality. In this segment, we’ll be sharing specific AR use cases we believe to be immediately practical and valuable for a range of industries.
Retail
Augmented reality is already being used in retail and e-commerce, mainly in the form of product demos and visualizations. For example, Sephora has created an application that lets users sample their beauty products via their front-facing smartphone cameras, prior to purchasing products directly.
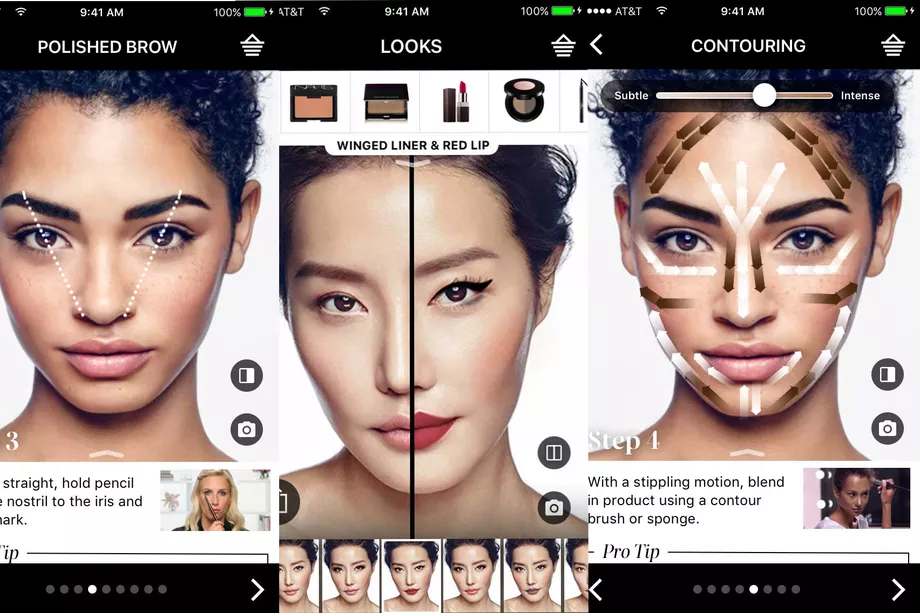
(source: The Verge)
Similar use cases have been adopted by Ikea, Wayfair, and Amazon, in which customers can place products into their houses to see how products would look in their environment. Product visualization demos can range from furniture and appliances - or even seeing what a new car would look like parked in your driveway.
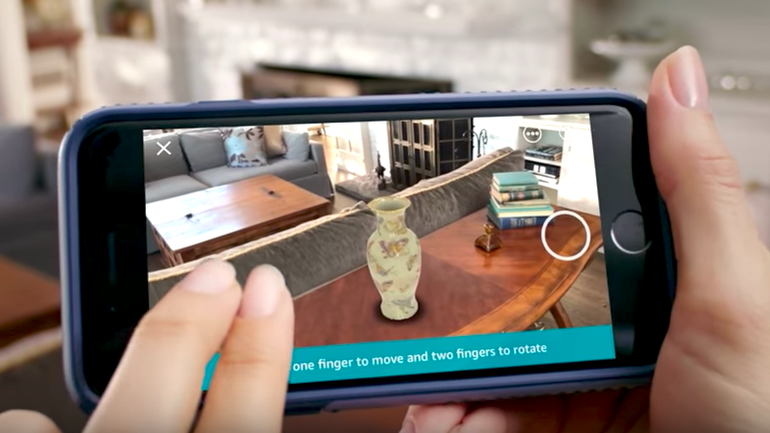
(source: ZDnet)
The multi-user and persistence capabilities of the AR Cloud, however, introduce new opportunities for retail. For example, a fashion outlet like Zara could pin floating digital notes to new outfits on sale as part of a summer lineup.
These notes could provide text, picture, and video information about the source of the fabrics, whether the material was organically and sustainably produced, and suggestions for other items of clothing that match well with the outfit. In an age where consumers are increasingly values-driven and impatient, making this information easily available to customers can be a competitive edge in sales.
Manufacturing
Augmented reality is already playing a crucial role in manufacturing, particularly in the product design process. You can see this in action in the video below, which explores how Ford is using Microsoft’s Hololens headset to improve their product planning:
AR headsets/glasses have already been adopted in manufacturing to streamline processes. An example of this in action is if an engineering team needs to undergo a training course to learn how to assemble a vehicle, ship, or any type of machinery. By using AR headsets like the hololens, the engineering team can quickly and intuitively understand how to use specific tools and components to build products or repair equipment that needs maintenance.
It’s also possible for these teams to asynchronously communicate with each other about key metrics or issues that arise. For example, an engineering project lead can walk around a worksite and see digital annotations, in real time, floating above various pieces of machinery to get a real-time glimpse of how a factory is operating.
Alternatively, if a piece of equipment is broken and needs repairing, the worker who identifies the problem can record a video of the damage and pin the video to that equipment - as well as “tag” relevant individuals about the issue, so that they can be promptly notified.
Thus, any other worker on-site would be able to find that video pinned to the equipment and understand the situation. The worker could then follow instructions from a remote technician to repair the equipment, streamlining operations all around.
Real Estate and Hospitality
The real estate and hospitality industries are a perfect fit for AR Cloud innovation, as they deal in the business of physical spaces and the experiences that people have in those places. Since AR is essentially an “internet of places”, where digital content is overlaid onto the real world, these industries will immediately benefit from new opportunities.
One immediate way that hotels can benefit is by improving the customer experience in guest rooms. This can be accomplished by providing interactive notes that can be pinned in a room, on top of specific points of interest. A concept demo of this for an Airbnb property is shown below:
By annotating properties with on-site contextual tips, hotels could provide a more seamless experience for visitors, as well as reduce the amount of live customer support needed regarding rooms.
Moreover, real estate agents could provide a more interactive experience for potential buyers by placing AR furniture and appliances in a property. With a click of a button, the agent could showcase dozens of different layouts and combinations of how an office or home could look once the property is set up.
Tourism
Three of the biggest questions tourists have when visiting a new city are:
How do I get around the city? Once I reach a tourist landmark, how can I learn more about that place? What have other tourists said about this place?
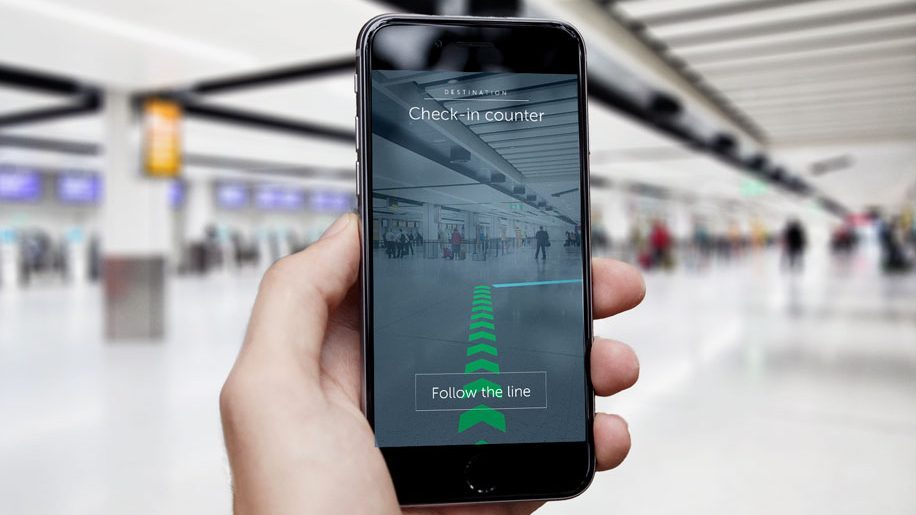
Wayfinding is one of the core benefits of the AR Cloud. GPS has provided us with the ability to generally navigate the world, but is frequently inaccurate within a range of 20 meters. Moreover, with its unintuitive birds-eye view, it can be difficult to know for sure if you’re heading in the right direction. Finally, GPS is useless indoors.
AR to the rescue! Advancements in computer vision and the AR cloud mean that tourists can navigate by following highlighted arrows and directions in their camera, instead of deciphering a confusing blue dot in Google Maps.

(Source: Business Traveller)
Ministries of tourism in cities around the world can use the AR cloud’s wayfinding capabilities to help tourists (especially foreigners) more easily navigate cities and large indoor destinations such as shopping malls, convention centers, and airports.
That said, finding a landmark is just the first step. AR cloud capabilities can provide tourists with a much richer, intimate, and contextual experience. For example, tourists may want to gain more information about a specific cathedral, historical site, or restaurant. In this case, it’s possible to create 3D animations of what a landmark looked like several decades in the past - as well as drop annotations and notes about specific spots at that landmark within an accuracy of millimeters.
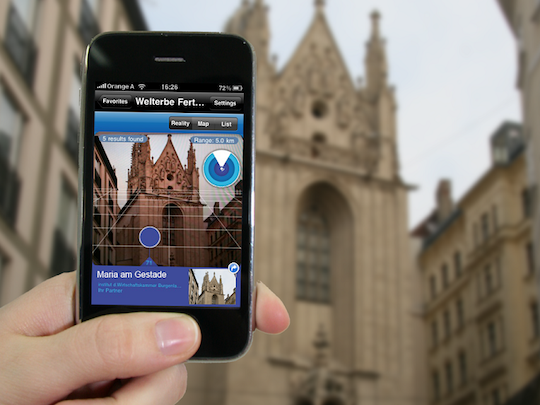
(Source: Business Computing World)
Websites like TripAdvisor have shown us that tourists are strongly interested in the opinions of other tourists. The AR cloud makes it possible for visitors to leave their own notes, tips, and feedback - in their own language - for future tourists to gain a better understanding of a city in a language and culture that they’ll understand.
This could include a Japanese tourist recording a video in a Roman Coliseum and dropping it at the front gate of the landmark, advising future Japanese tourists to inquire about events that might be happening nearby.
Multiplayer AR Games
Pokemon Go is a gaming phenomenon that exploded in popularity and proved the viability of AR games as a business opportunity. To date (in summer 2018), users have been spending $2M USD, DAILY, in this AR experience.
It goes without saying that multiplayer AR games present a massive blue ocean opportunity, as this type of gaming experience is completely novel and largely uncharted territory. Games powered by the AR Cloud will enable users to interact with characters, assets, and content that conform to the real world.
That is, it’s possible to create a giant multiplayer game of laser tag or PacMan in an office or outdoor park. Users can stick an AR basketball hoop to a wall and simultaneously shoot digital balls at the hoop to try to win a top score. The physical world as we know it can become the playspace for these gaming environments, instead of being limited to the form factor of a smartphone or TV screen.
Interested in building an AR application? Get in touch!
We are at the cusp of the next frontier of computing: an entirely new type of internet that overlays the real world, instead of being limited to 2D icons on smartphone screens.
The shift into augmented reality will be as transformative and disruptive as the emergence of the internet and the rise of mobile. Companies who capture the potential now can gain a strong advantage over their competitors - or pioneer breakthrough products that shake up established industries. We at Xmartlabs have built a team capable of delivering all of this potential - and beyond. Let's talk!
