
Well-informed, objective decisions have always been a key aspect of every successful business. Nowadays, lots of companies gather a huge amount of data as a result of different processes, i.e, marketing campaign results, web site analytics or customer information on their product databases such as usage history or demographics. Once you have this input, a key component in today's data-driven company is the data warehouse. There, a consolidated view of all the convenient business information is stored in one place and can be queried in-depth for complex analysis.

(source: Cazena)
Cloud Data warehouses are a popular choice among today's options. This type of warehouses are easy-to-scale, highly performant and cheaper than their in-house counterparts, as companies don't need to buy and maintain dedicated hardware nor hire highly specialized personnel.
On this ecosystem of providing a data warehouse as a service, there are two solutions that you must have heard about, especially if you prefer AWS platform, Amazon Redshift and Snowflake. With Columnar storage and massively parallel processing (MPP) infrastructure, integrated with many Business Intelligence solutions and flexible pricing, this two solutions will definitely meet most of your requirements to analyze your business data today and in the future to come.
However, choosing the right option for your company sometimes is not about if the solution will successfully complete a task but what is the most suitable option for your data strategy. Following, we describe some aspects that are different between these two solutions and you should have in mind when choosing your data warehouse.
Pricing
One of the questions that may arise when selecting a warehouse is, what will I pay for?
The Snowflake approach for pricing is essentially paying for what you use, splitting the billing on:
-
Computing:
- Offers a compute resource called Warehouse, which comes in seven different sizes.
- The price is charged per-second of warehouse usage, which can be configured to automatically stop and resume.
- Each second cost a fraction of a credit. The price of the credit varies on the plan you selected.
-
Storage:
- On-demand: Pay storage as you use it on a monthly basis.
- Up-front: If you know how much storage you need, you can pre-pay for it each month, which is cheaper than the on-demand option.
The pricing on Redshift is more coupled but it offer some interesting options too:
- You can choose between two different cluster types, dense compute or dense storage, both options with powerful characteristics.
- The usage is billed on a per-hour granularity.
- You can choose between an on-demand plan or an up-front payment, obtaining interesting savings if you choose the latter option.
- Provides a Concurrency Scaling option, where you can add to your cluster more computing power on-demand, priced on a per-second rate.
- Amazon now provides Redshift Spectrum, which allows the user to run queries over S3 storage data. This way, you can pay for your storage and compute capabilities more independently.
Security
If you manage sensitive information, for example, Protected Health Information (PHI), one of your top concerns must be to have an infrastructure that correctly protects your data and complies to the highest standards.
Redshift provides robust and customizable end-to-end encryption, network isolation using VPCs and audit options through CloudTrail integration, among other features. Also, AWS services comply with several programs, meaning you can configure your cluster to satisfy well-known regulations.
Snowflake also takes security seriously and provides always-on encryption on both your in-transit and at-rest data, VPN network isolation and also complies with security regulations. The important detail here is that these security options will depend on the plan you selected, so you should take extra care when selecting the plan that fits your needs best. For example, if some of the data you want to analyze are PHIs, you must at least have an "Enterprise for Sensitive Data" plan, which is the first level that provides HIPAA support.
Performance
A desirable feature for your data warehouse is the ability to scale up or down the compute capacity as your needs change. On Snowflake, this process is as easy as altering your warehouse and select a new size, taking virtually no time.
On redshift, you have two different options to re-scale a cluster:
- Elastic resize:
- Change only the number of nodes on your cluster
- Takes a few minutes to add the new resources and redistribute the data among them.
- Classic resize:
- Change the types of the nodes (and the amount if you want).
- Takes some hours, as a new cluster is created the data from the old one is transfer to it.
- Redshift team recommends to follow the approach Snapshot, Restore, and Resize to avoid downtimes during this process.
Another topic to consider is how to manage the query load on your data warehouse, in order to deliver the needed information for every report in a reasonable time.
On Redshift, all the user that wants to analyze data on the cluster shares the compute resources, so if there are a lot of user running a bunch of queries, they will definitely compete for them. The solution that Redshift provides to control this concurrency problem is to configure WLM Queue Assignment Rules to give priority on the cluster usage.
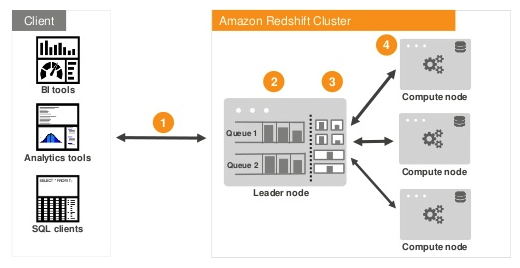
(source: Amazon)
On Snowflake, the solution is much simpler, as the data and compute layers are independent. On this platform, you can create different warehouses for different proposes and give each one different compute capacities if needed. This way, different queries to different warehouses won't compete, as they have separated resources.
(source: Snowflake)
Semi-Structured data
Nowadays, it is more and more common to have information on a semi-structured format, for example, a JSON report from 3rd party API like Google Analytics Reporting API or exports from a NoSQL database like MongoDB.
If this is the case and you want to extract and correlate this data with other sources, Snowflake provides out-of-the-box datatypes and a query syntax that allow you to traverse your JSON data. Redshift also provides this feature through Spectrum, but it needs some previous configuration to work properly, like creating external schemas and tables.
Summarizing, both of these cloud data warehouse options are powerful and flexible solutions that are constantly improving to help companies to focus on what's important, get data-supported insights that will make their business successful.
