
Introduction
In this blog post, we will introduce Apache Kafka, how it works, some of its use cases, and a comparison against RabbitMQ and Amazon SQS.
Kafka is highly useful when trying to connect services without coupling them, creating real-time communications, managing streaming data sources, and more. We will cover the details about this in the use cases section.
What is Kafka?
Apache Kafka is not just a messaging system; it’s an open-source distributed event streaming platform for high-performance data pipelines, streaming analytics, and data integration.
While creating a messaging system using other methods and tools is possible, these solutions can quickly become problematic as system loads and stress increase. That's where Kafka shines and becomes the ideal solution.
Some key features:
- High throughput: the ability to process huge amounts of messages per second
- Scalability: the ability to grow in capacity when the load increases
- Fault-tolerant: if a node loses a message, another one should have a copy of it
- High availability: if a node breaks, another one should be able to respond
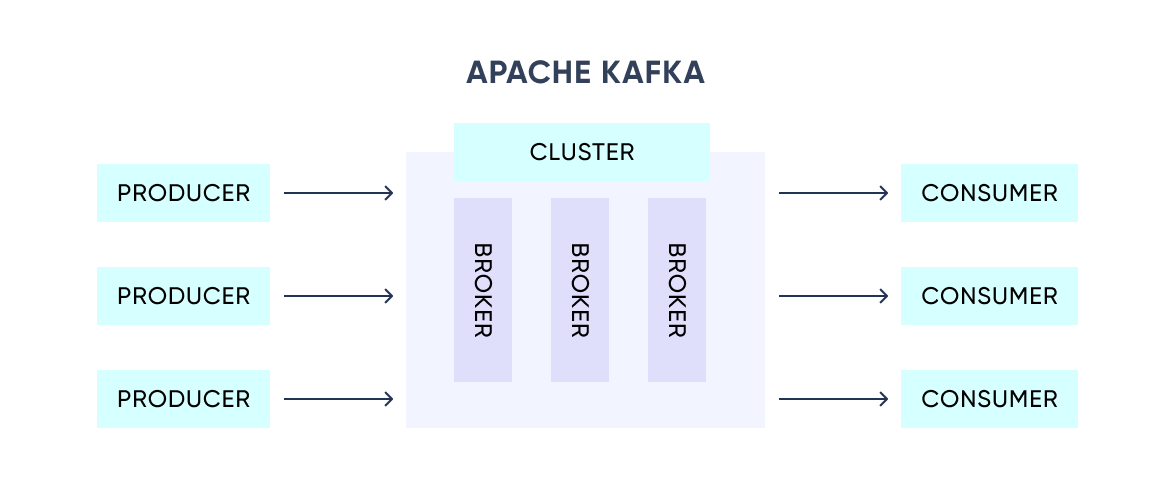
Understanding the Kafka Architecture
Kafka is a distributed system that receives producers' events and sends them to consumers via a high-performance TCP protocol. Each event is a key-value message.
Events are organized into topics, and topics are partitioned. Each event in a partition is identified by a sequential number called offset which is assigned on message arrival. Events with the same key (denoted by their color in the figure) are written to the same partition.
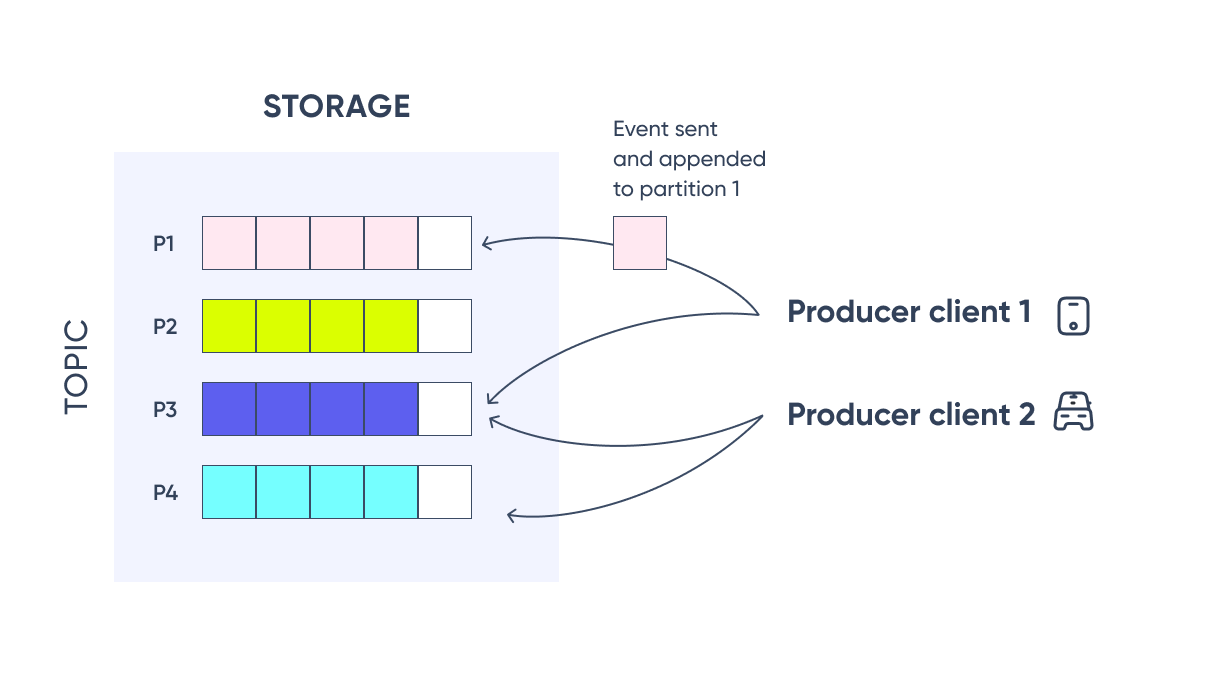
Unlike traditional messaging systems, events are not deleted after consumption. Instead, it is possible to define for how long Kafka should retain events
Apache Kafka Use Cases
This section will explore some of the most common use cases for Kafka, including messaging, website/app activity tracking, metrics and log aggregation, stream processing, and event sourcing. We'll also take a closer look at how Kafka connectors can easily solve some specific use cases.
- Messaging: using Kafka, two or more software components can communicate with each other in real-time and without coupling.
- Website / App Activity Tracking: nowadays every website or app tracks users’ activity. Kafka can be used as a receiver of those events and relay them afterward. The consumers of those events are then able to analyze the activity for decision-making.
- Metrics and log aggregation: when different components have their own metrics and logs, Kafka could be the touch point to centralize them into one place.
- Stream processing: when a data pipeline needs to process a streaming data source, Kafka can be used as a source and destination of each step of the pipeline before storing the data into its final destination.
- Event sourcing: for event-driven or even micro-service architectures, Kafka could be the component in charge of the communication between each service. This is the case in which one software component needs to react as a result of another component's execution.
- Some use cases can be solved just by setting up the already developed Kafka connectors: https://docs.confluent.io/kafka-connectors/self-managed/kafka_connectors.html#kafka-connectors
Comparison between Kafka and other Messaging Systems
Of course, when choosing a messaging system for your streaming data pipeline, Kafka is not the only alternative, and several options are available in the market. RabbitMQ, and Amazon SQS are two of the most popular messaging systems used today, each with its own unique strengths and weaknesses. In this table, we'll compare these three messaging systems across five key areas so you can make an informed decision on which messaging system best fits the needs of your application.
| Application size | Hosting | Message delivery | Message order | Goal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kafka | Big to Huge | Self-hosted | At least one delivery | Order may change | Scalability & Performance |
| RabbitMQ | Medium to Big | Self-hosted | Guarantees only once delivery | Order may change | Scalability & Performance |
| Amazon SQS | Small to Medium | Managed | Guarantees only once delivery | Maintained on FIFO queues | Simplicity |
Best Practices and Advice
Proper use of Kafka is crucial to efficient performance and smooth data processing. Here are some key things to keep in mind when using Kafka for messaging and data streaming. These practices can help you optimize performance, ensure data durability, and protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Properly size your Kafka cluster: Properly size your Kafka cluster to handle your expected message traffic. A Kafka cluster can be scaled horizontally by adding more brokers to the cluster, but it's important to ensure that the brokers are sized appropriately for the expected message traffic.
- Use replication for data durability: Configure replication for your Kafka topics to ensure data durability in case of broker failures. A replication factor of at least 3 is recommended to ensure that data is available even if one or two brokers fail.
- Monitor your Kafka cluster: Monitor your Kafka cluster to ensure it is healthy and performs optimally. Use tools like Kafka Manager or Burrow to monitor Kafka metrics such as broker health, topic and partition status, and consumer group lag.
- Use consumer groups for scalability and fault tolerance: Use consumer groups to scale your Kafka consumers and provide fault tolerance. Consumer groups allow multiple consumers to work together to consume data from a topic, which allows for higher throughput and better utilization of resources.
- Secure your Kafka cluster: Secure your Kafka cluster to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Use authentication and authorization mechanisms such as SSL/TLS and ACLs to ensure that only authorized users and applications can access your Kafka cluster.
Conclusion
Apache Kafka is an invaluable tool for high-performance data streaming and management. As a solution architect, it's important to understand its internal design and compare it with other available tools to determine the best solution for your needs. However, simply selecting Kafka is not enough. Implementing it requires careful consideration of best practices, especially those mentioned above. By following these best practices, you can ensure your Kafka implementation's optimal performance and security.
If you're interested in learning more about how Apache Kafka can benefit your business, or if you have any questions, feel free to contact us at Xmartlabs. Our team of experts is always ready to help you.
