
In the LinkedIn-dominated reality we currently inhabit, the pursuit of success often comes at a steep price. Workaholism, defined as an excessive and compulsive dedication to work, has emerged as a significant concern in our modern professional landscape. While remote work is becoming more popular and offers positive outcomes for both employees and organizations, it has blurred the lines between work and personal life, potentially exacerbating workaholic tendencies.
If you've ever found yourself constantly checking work emails during family dinner or felt guilty for taking a day off, you're not alone. This blog will explore the profound effects of workaholism, which extends far beyond the confines of the office. We'll delve into the underlying factors contributing to this phenomenon, examine its social implications, and discuss practical strategies for achieving a healthier work-life balance.
Understanding Work Addiction
Workaholism is characterized by two primary dimensions: working excessively and working compulsively. Individuals exhibiting workaholic tendencies tend to devote an extraordinary amount of time to their work, surpassing what is considered reasonable. Additionally, they feel a strong internal pressure to work hard and constantly think about work, even during off-hours.
According to a 2022 study by the American Psychological Association, approximately 25% of working adults exhibit workaholic behaviors, highlighting the prevalence of this issue.

Social Context and Risk Factors
Several factors of today's fast-paced world contribute to the rise of workaholism:
- Global Economic Pressures: The demands of the global economy drive companies to constantly innovate and compete, creating an environment where employees feel compelled to demonstrate unwavering commitment.
- Company Culture: Organizations that reward excessive commitment and overtime inadvertently encourage work addiction.
- Technological Advancements: The omnipresence of smartphones and remote work tools has made it possible to work from anywhere at any time, blurring the boundaries between work and personal life.
- Psychosocial Factors: Contemporary work structures introduce psychological and social risks, contributing to new forms of psychological disorders such as workaholism.
Various personal and organizational factors contribute to the development of work addiction:
- Economic pressures at home
- Fear of job loss
- Intense competition in the labor market
- The pursuit of success and achievement
- Fear of opposing managerial demands
- Poor organizational management
- Conflicted home environment
Recognizing these multifaceted factors is crucial in addressing work addiction effectively.
Consequences of Workaholism
While hard work and dedication are generally positive traits, workaholism takes these to an unhealthy extreme. The consequences of work addiction can be far-reaching and severe:

Mental Health Issues
- Increased vulnerability to anxiety, depression, and burnout
- Chronic stress leading to emotional exhaustion and loss of motivation
Physical Health Deterioration
- Fatigue and weakened immunity
- Increased risk of cardiovascular problems
- Neglect of rest, recovery, and proper nutrition
Strained Relationships
- Isolation from friends and family
- Communication breakdowns with loved ones
- Neglect of personal life commitments
Decreased Productivity
- Cognitive fatigue reducing focus and decision-making abilities
- Increased risk of burnout, ultimately lowering overall productivity
Impact on Work-Life Balance
- Little time for relaxation or hobbies
- Exacerbation of stress and emotional exhaustion
Social Impact
- Glorification of overwork contributing to widespread burnout
- Promotion of unhealthy work norms
- Increased public health risks related to work-related stress
Career Burnout
- Plummeting job satisfaction
- Disengagement and lower performance
- Higher turnover rates in organizations
Technology and Remote Work: A Double-Edged Sword
Advancements in technology and the rise of remote work have transformed how we work. While they offer flexibility, they also present challenges related to workaholism.
- The Always-On Culture
With smartphones and constant connectivity, employees are accessible 24/7. This "always-on" environment can blur work-life boundaries, create expectations for immediate responses, and encourage checking work during personal time.
- Remote Work: Flexibility vs. Overwork
Remote work has become the norm, offering flexibility and eliminating commutes. However, it can also make it harder to "switch off," extend work hours, and blur the line between work and home.
- Digital Overload and Productivity Pressure
Digital tools, while useful, can lead to information overload and increased pressure. Constant interruptions from communication platforms and performance-tracking tools can make employees feel perpetually behind.
- Social Isolation and Lack of Human Interaction
While remote work allows for more independence, it can also lead to feelings of isolation due to the reduced face-to-face interaction with colleagues. This can negatively affect mental health and collaboration, leading to disengagement over time.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing and managing workaholism requires a multi-faceted approach involving efforts at both individual and organizational levels. Let's explore strategies that can be implemented by individuals and companies to foster a healthier work-life balance.
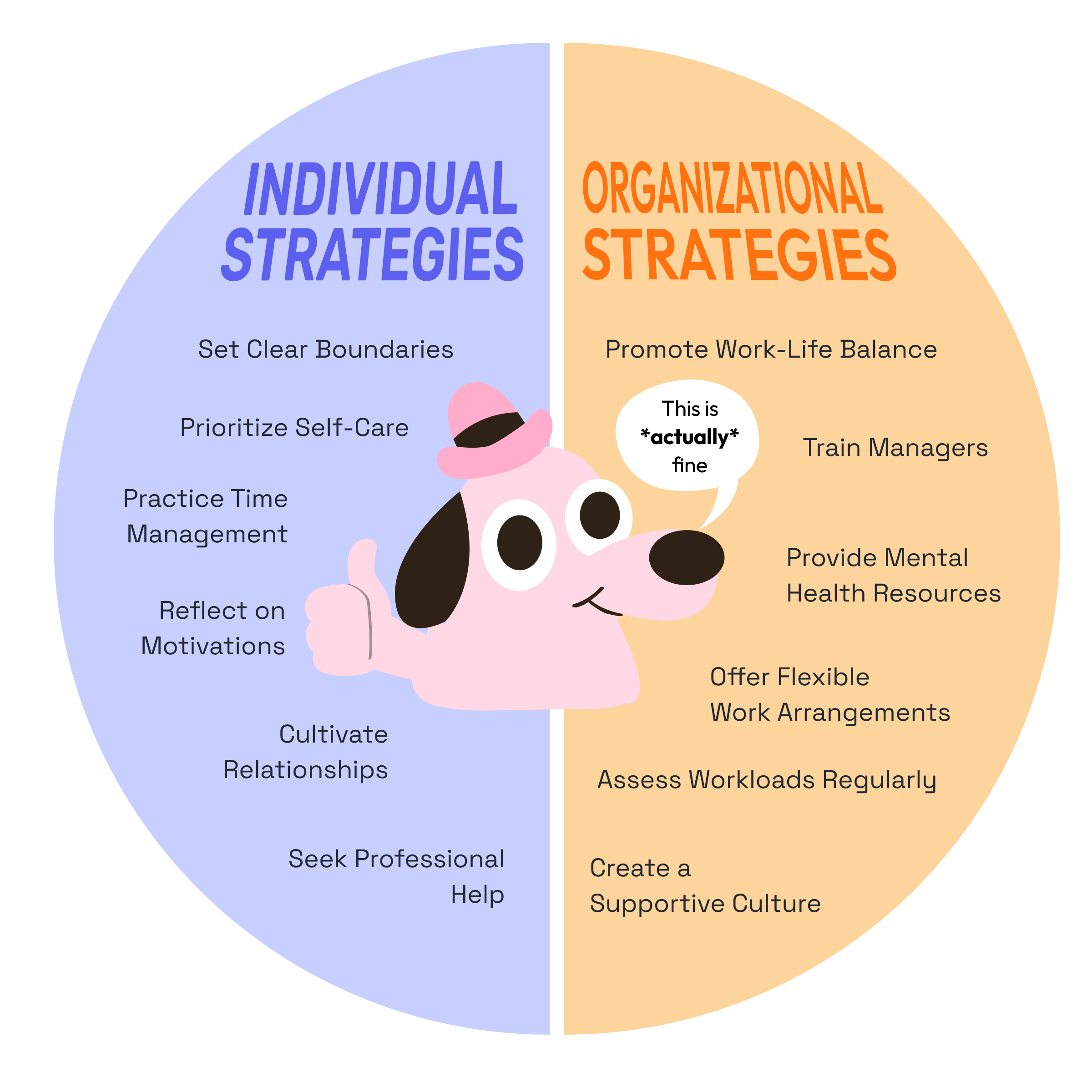
Individual Strategies
As an individual, there are several steps you can take to prevent workaholic tendencies:
- Set Clear Boundaries: Establish specific work hours and stick to them. Avoid checking work emails or taking calls outside of these hours.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Make time for activities that promote physical and mental well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies.
- Practice Time Management: Use techniques like the Pomodoro method to work efficiently and take regular breaks.
- Cultivate Relationships: Invest time in personal relationships and activities outside of work.
- Reflect on Motivations: Understand what drives your work behavior. Are you working out of passion or to avoid other aspects of life?
- Seek Professional Help: If you're struggling to manage work-related stress or compulsions, don't hesitate to consult a mental health professional.
Organizational Strategies
Companies play a crucial role in preventing workaholism. Here are some strategies organizations can implement:
- Promote Work-Life Balance: Encourage employees to take time off and respect their non-working hours.
- Offer Flexible Work Arrangements: Allow for flexible schedules or remote work options when possible.
- Provide Mental Health Resources: Offer access to counseling services or Employee Assistance Programs.
- Train Managers: Educate leadership on recognizing signs of workaholism and how to support team members.
- Assess Workloads Regularly: Ensure that job demands are reasonable and achievable within normal working hours.
- Create a Supportive Culture: Foster an environment where efficiency is valued over long hours.
At Xmartlabs, we strive to implement many of these strategies to create a healthy work environment. We offer flexible hours and the option to work remotely or in the office, giving our employees more control over their work-life balance. We actively promote a balanced lifestyle and make conscious efforts not to encourage workaholic behaviors.
While we recognize that there may be exceptional circumstances requiring additional effort, we ensure these situations are not the norm. Our goal is to create an environment where productivity and personal well-being go hand in hand, fostering long-term success for both our employees and the company.
Remember, preventing workaholism is a shared responsibility. While companies should strive to create healthy work environments, individuals also need to be proactive in maintaining their work-life balance. By working together, we can foster a culture that values productivity, creativity, and personal well-being.
Conclusion
Often, we link success with working too much, but the hidden costs of workaholism can't be ignored. As we've seen, work addiction is caused by a mix of personal, social, and job-related factors. This addiction can harm mental and physical health, damage relationships, lower productivity, and make it harder to enjoy life.
The rise of technology and remote work has made things worse, blurring the line between work and personal time. The "always-on" culture, constant digital demands, and feeling isolated while working from home make it harder to step away from work.
However, both individuals and organizations can take steps to prevent workaholism. We can reduce its impact by setting clear limits, taking care of mental and physical health, and encouraging a better balance between work and personal life.
In the end, fighting workaholism is a shared effort. Employees need to take care of themselves, and companies should help by creating a healthier work culture. Together, we can build a work environment where productivity and well-being go hand in hand.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from work-related mental health issues like workaholism, try to reach for help, and remember you're not alone.

